This resarch paper is inspired from azeria If you wanna learn and understand more I will provide resources in comment section.
Introduction of Heap and Memory
As we all know Our memory consist of various data segments like HEAP, STACK, DATA, BSS, GOT, PLT, TXT as you can see in this architecture this is a memory region consist of those data segments

BSS & DATA- conatins variables and pointers used in program
TXT- contains executable with assembly
PLT & GOI- contains specific pointers
These all resdides in program code whereas Heap and stack are used for allocating region in memory and storinbg the local variable respectively These resarch paper is all about the Heap so we don’t talk about stack in this article
Heap and memory curruption
Heap is used by program to allocate region during program execution. the allocation took place with the help of malloc function when the program finises then the heap manager return the allocation back to heap with the help of function free. In other words malloc is used for allocating the region while free is used for free the allocated region
Since, heap and stack are memory regions and the data which is stored and allocate in this region is provided by user as user input variable so user can overwrite eip registers, remote code execution, overflow the heap and stack etc. This all can be done by injecting payload in memory region and it’s called Memory Curruption. Memory curruption bug leads to modification of memory that leads to remote code execution, overflows etc.
Strategies of Heap To Allocate Chunks
Basically heap works on four strategies to allocate a chunk to a region of memory I will depict all the four steps used by heap manager to allocate chunk. CHUNKS are the area of memory in heap whis is dynamically allocated via malloc. Now, the four steps are:
=> Allocation from free chunks
This strategy says that if a previous chunk of memory if free by free function and that chunk is large enough to satisfy the request of allocation then heap will use that chunk The free chunks are located in the link list called bins whenever the heap manager needed allocation it searches in the bins for the free chunks that satisfy the request of allocation If they found the free chunk in bins then they extracted it from bins and mark the chunks as allocated That’s how the strategy works
=> Allocation from top of heap
Suppose, our first strategy failed i.e the heap manager can’t find the free chunks in bins that satisfiy the request of allocation. Then, heaqp manager will follow second strategy i.e heap manager will looks at the bottom of heap which is also called as top chunk If there is space at left at the bottom of heap then heap manager will allocate chunk from there
=> Asking Kernel for memory at top chunk
If both strategy failed i.e heap manager can’t find any free chunks in bins and also there is no space at top chunk then heap manager will ask from kernel to add some memory at the top chunk with the help of system call sbrk This system call is used in linux/unix operating sytem to increase the amount of memory in heap region But there is one drawback of this system call it increase too much memory of heap that leads to collapse of heap with other libraries. So, for solving this issue we use the syscall called mmap Once the heap reaches to it’s point we call mmap syscall for not expending the heap more then it’s limit
=> returning Null
If all stratagies fails, then there is no option left for heap manager. since, there is no memory allocation malloc will return NUll
strategies in short visulization
- Allocation of previously used chunk
- If there is space at top chunk then use it
- otherwise ask kernel to add memory at top chunk
- If all fail then malloc will return null
Concept of Arenas In Heap
In single threadedpplication there was only one main arena so other processses have to wait untill the first one one is completed it consumes too much time In heap each Arena manages its own chunk allocation and free bins separately Main arena consist of main heap when the process starts to increasing the heap will provide second arena so that it reduce the time for waiting of thread to perform operations likes malloc and free With each new thread heap will provide diffrent arena once the limit of arenas if finished then heap has no option left except for sharing the arena with other process Second arean is created by sub heaps using the system calls mmap and mprote
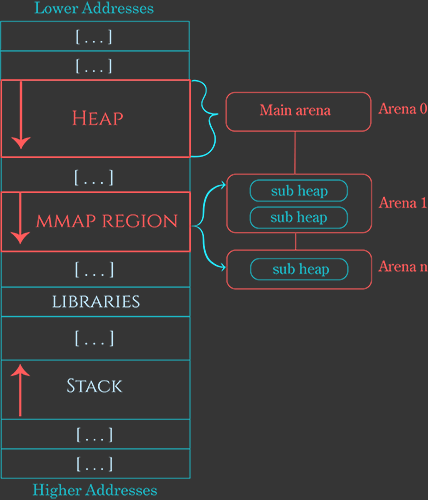
In arenas there is also a concept about subheap. Heap is same as Sub Hesp except Heap loaded in memory as program executed and expended by sbrk system call while the sub heap is loaded in to memory by using syscall called mmap and heap manager grow the sub heap with mprtotect to avoid memory currutption When a Heap want to create a sub heap it ask kernel to reserve a space in moemory for subheap so that sub heap can grow with the syscall mmap
In the next post i will cover up the types of bins, flags and recycling free chunks strategies used in chunks For further reading i will add the resources you can learn from therte about heap more :
*If you wanna ssupport me for more articles you can donate me on my upi id: *mohit6398@dbs